Chapter 2.4 - Discuss how variables are used in a program | Part -1
DECLARATION OF VARIABLES
After designing suitable variables names, we must declare them to the compiler.
The declaration does two things:
- It tells the compiler what the variable name is.
- It specifies what type of data the variable will hold.
C language tutorials for beginners
Download Let us C eBook | by Yashwant Kanetkar
Primary Type Declaration
A variable can be used to store a value of any data type. That is, the name has nothing to do with its type. The syntax of declaring a variable is as follows:
data-type v1,v2,....vn
v1,v2,...vn are the names of variables. Variables are separated by commas. A declaration statement must end with a semicolon. For example, valid declarations are:
int count;
int number, total;
double ratio;
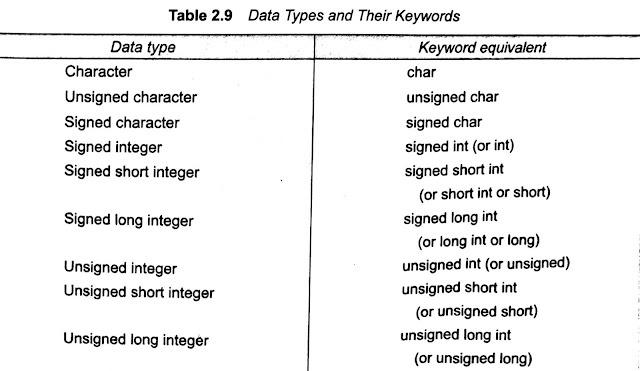
int and double are the keywords to represent integer type and real type data values respectively. Table 2.9 shows various data types and their keywords equivalents. #variables_in_c
The program segment given in Fig 2.7 illustrates the declaration of variables. main() is the beginning of the program. The opening brace { single the execution of the program. Declaration of variables is usually done immediately after the opening brace of the program. The variables can also be declared outside (either before or after) the main function. The importance of the place of the declaration will be dealt with in detail later while discussing functions. #allaboutprogramming62
Note-: C99 permits declaration of variables at any point within a function or block, prior to their use
When an adjective (qualifier) short, long, or unsigned is used without a basic data type specifier, C compilers treat the data types as an int. If we want to declare a character variable as unsigned, then we must do so using both the terms like unsigned char
Default values of Constants
Integer constants, by default, represent int type data. We can override this default by specifying unsigned or long after the number (by appending U or L) as shown below:
Literal Type Value
+111 int 111
-222 int -222
45678U unsigned int 45678
-56789L long int -56789
987654UL unsigned long int 987654
Similarly, floating point constants, by default represent double type data. If we want the resulting data type to be float or long double, we must append the letter f or F to the number for float and letter l or L long for long double as shown below:
Literal Type Value
0. double 0.0
-222 double 0.0
45678U double 12.0
-56789L double 1.234
987654UL float -1.2
1.23456789L long double 1.23456789
Top 10 Useful Basic Commands for Linux Users
C Pattern Programming Example Tutorial
Top 10 Useful Basic Commands for Linux Users
C Pattern Programming Example Tutorial




Comments
Post a Comment
Ask Me Everything About Programming.